Carbs, Fat Burners & Energy: What Really Works?
aerobix
Should athletes follow a low or high carb diet ?
As we all know we get energy from our foods and we can’t make energy , we can only transfer it to something else. Just like we phone uses a battery, our cells uses a specific substance called Adenosine Triphosphate (ATP ) for energy. We need ATP for nearly every action in our body.
There are three main energy systems are in our body;
- ATP – PCr System
- Glycolytic Path Way
- Oxidative Phosphorylative Pathway
- ATP – PCr System run out quickly, but give us a blast of immediate energy for movements that require power, force , speed , and other intense activities ( such as sprinting ).
- Other energy systems provide sustained energy but a lower pace , which means we have to move at lower inensity.
Our energy systems are always working together in someway. However, depending on the activity type, on system may dominate.
if we think about sports in general, we can see that most are about in exceeding limits ; running faster, jumping higher, pushing harder, lifting heavier and so on. Few are low intensity.
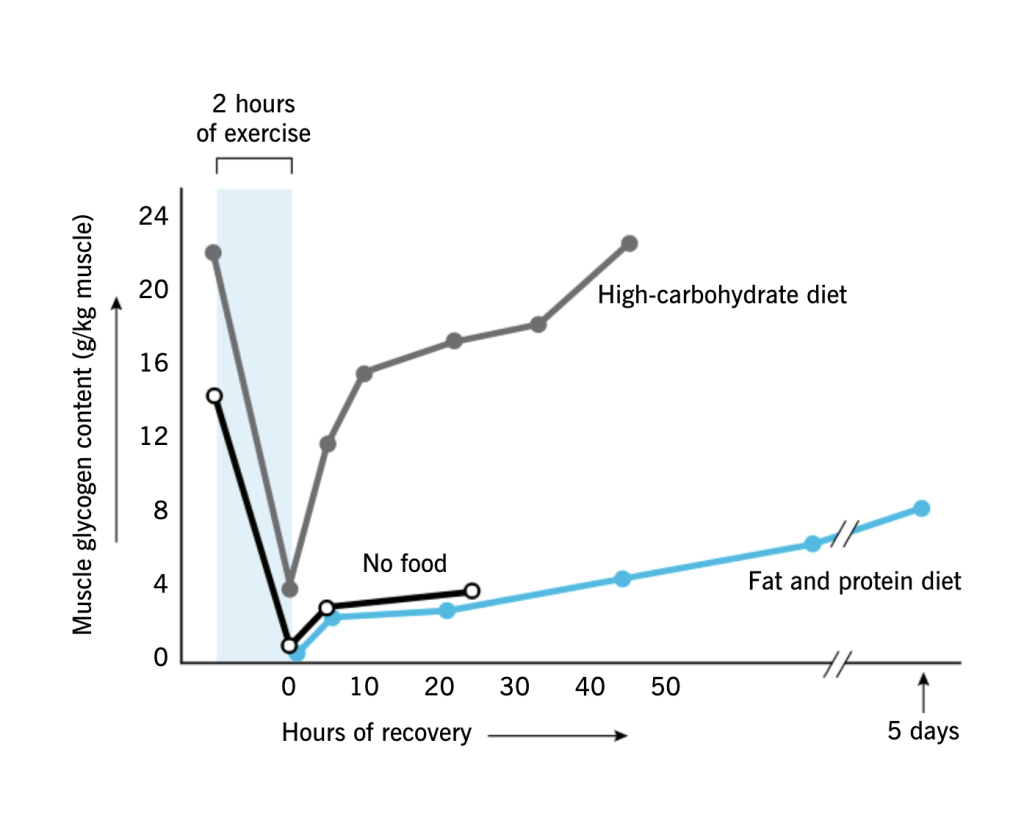
Figure : Muscle glycogen content VS Different Types of Diets
Performance
The amount of carbohydrate consumes by the athlete will probably affect the energy that’s available for performance.
Based on the performance data of athletes and fast ATP production from carbohydrates, suggest that a higher carbohydrate intake helps most athletes train longer at moderate or high intensities and feel less fatigued.
Recovery
During recovery time carbohydrates take major role to replace the glycogen that we used during intense movements.
We suggest that , if we consume carbohydrate in two to three hours immediately after intense workout, this will help glycogen rapidly replaced, which means our recovery will be better and , we’ll be able to train tomorrow again .
Do “Fat Burning Supplements” work ?
When Adrenaline & Noradrenaline hormones go up , it tells the body release fatty acids into the bloodstream for energy.
These hormones can go up for a few reasons. Exercise and stress are two of the most common.
All ‘ fat burning supplements ‘ contain stimulants, such as caffeine, that amp up our ‘ fight or flight ‘ hormones. As a result they lower our appetite temporarily.
So the fats may be released, but if we’re not exercising, they don’t do anything. Eventually they shrug and go back home again.
Stimulants don’t give you energy, instead stimulants borrow energy. And if we don’t use energy, it gets put back, often leaving us feeling less energetic than before.
But if we are combine mid stimulants with an exercise session where those fatty acids can be used.
How do we get Fat ?
We package and store fats when we eat more than we burn through metabolism and activity.
- Excess dietary fat is directly stored as body fat.
- Excess carbohydrates increases carbohydrate oxidation, and causing more dietary fat to be stores as body fat.
- Excess Protein increases protein oxidation, impairing fat oxidation, and causing more dietary fat to be stored as body fat.
this means no matter what combination of macronutrients you eat, if you eat more than you expend, you’ll store the excess energy as fats.
Why Your Body Loves Fat
Fatty acids and triglycerides have several key roles in our body ;
- They provide structure of our plasma membranes, and make up a large proportion of fatty tissues such as our eyes or brains.
- They provide raw materials for many hormones, and help regulate the function of other hormones.
- They’re largest fuel depot in the body.
- They help us regulate our body temperature.
- They provide crucial nutrients.
Fat is involved in the energy transfer process in several important ways .
The creation of new fat takes place mostly in the live, although it can also happen in fat tissues when energy intake from food is high, energy output from metabolism and activity is low, and when insulin is high.
